Triangle > Acute Triangle
ACUTE TRIANGLE
Definition
An acute triangle is a 2D shape that has ALL THREE ANGLES LESS THAN 90°.
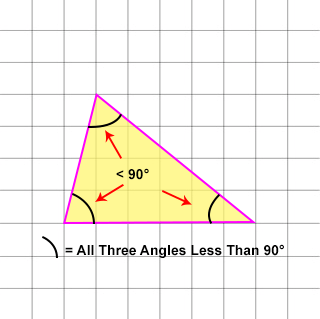
INTERESTING FACTS:
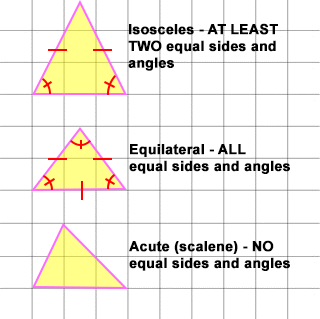
- An isosceles triangle is a triangle with AT LEAST TWO equal sides. As a result it has two equal angles. Isosceles is derived from the Greek iso (same) and skelos (leg). An isosceles right triangle is a special kind of isosceles triangle.
- An equilateral triangle is a triangle with ALL equal sides. An equilateral triangle is a special kind of isosceles triangle.
- A scalene triangle is a triangle with NO equal sides.
- There are three shapes (
 ) that have equal parts :
) that have equal parts :
- A SQUARE has all equal sides.
- A ISOSCELES TRIANGLE has all equal sides and angles.
- A CIRCLE has all equal radii and diameters.
It Is Helpful To Think
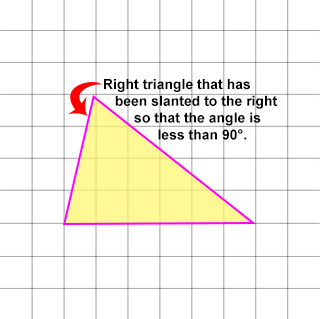
It is helpful to think of an ACUTE TRIANGLE as a RIGHT TRIANGLE whose right angle has been changed to be LESS THAN 90°.
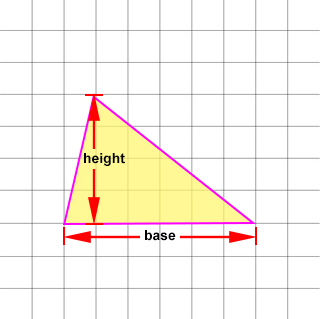
Traditional Formula
AreaTriangle = ½(base x height)
NOTES:
- BASE is normally the distance along the bottom of the triangle. However, the base can be any side as long as the height is measured at right angles to the base.
- HEIGHT is measured at a right angle to the base to the highest point on the triangle.
- This formula works for all triangles.
INTERESTING FACT: The three angles always add to 180°.
Thinking Inside The Box
If you place an ACUTE TRIANGLE inside of a box (a square or a rectangle), you can think of the acute triangle as a "slanted" right triangle which can be thought of as a half of a square or rectangle. (See right triangle section for details)
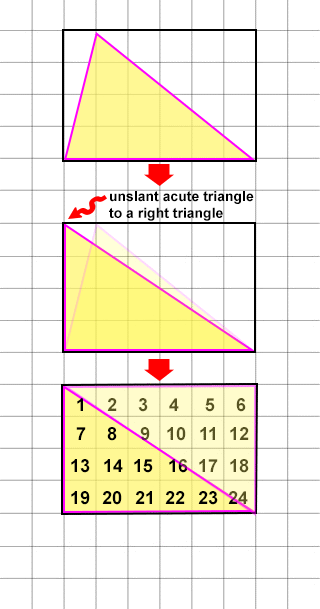
KEY: Instead of having to learn another formula (AreaTriangle= ½(base x height)), simply use the rectangle formula in its place and divide the result by 2 to get half of it.
Example
An acute triangle with a base of 6 in and a height of 4 in has an area of:
- Treat the base as the width.
- Use the rectangle formula instead (AreaTriangle= height x width).
- Divide the result by 2.
AreaTriangle = (4 in x 6 in)/2 = 24 in/2 = 12 in2
REFERENCE: See screenshots above for graphic representations.
Memorization Tips
- To remember the similarities between a triangle and a kite, It is also helpful to think of a TRIANGLE or a KITE as HALF of a rectangle or a square. Hence, you divide the result by two.
- It is helpful to think of an acute triangle as "a cute" (pretty) triangle because you can measure its height from WITHIN the triangle. Unlike the obtuse triangle, you have to measure its height from OUTSIDE the triangle because one of its angle must be greater than 90°.
- Like a parallelogram is thought of as SQUARE or RECTANGLE that has been "pushed" from the top, it is helpful to think of an acute triangle as a right triangle that has been "pushed" from the TOP.